Historical Content Alert
This is a historical content for Windows NT 4.0 product and is presented for informative purposes only. All content in this directory is copyrighted and owned by Microsoft.Certificate Enrollment
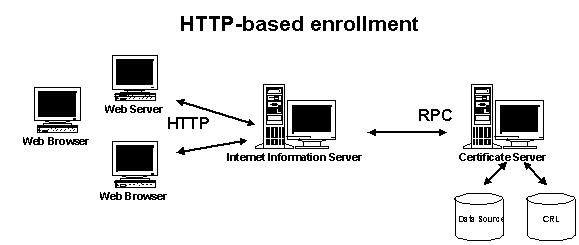
As illustrated in the following diagram, HTTP-based enrollment is handled by Microsoft® Internet Information Server (IIS) which uses Remote Procedure Call (RPC) to communicate with Microsoft Certificate Server. The IIS server can be hosted locally on the same machine as the Certificate Server or on a remote server. The enrollment code on the IIS server can also be configured to talk to multiple Certificate Servers by supplying the name of a specific Certificate Server in the call to the Server Engine. For example, an organization might use a separate Certificate Authority (CA) for each division to provide flexibility over policies and key management. If this is the case, the enrollment code would then supply the name of the Certificate Server for the user's division when making the call to the Server Engine.
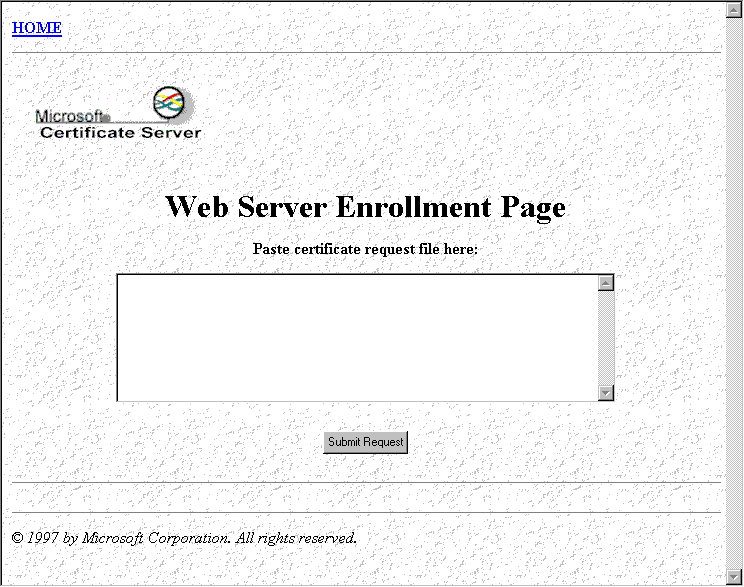
The IIS server has a series of HTML forms that allow the user to request certificate types if applicable and any identifying information that the CA needs in order to validate the request and generate the certificate. The enrollment code that ships as part of Certificate Server offers two methods for validating the user's identity:
-
Authentication through the user network logon.
- Authentication through a database lookup by the Policy Module on the user name, e-mail address and employee identification number.