Historical Content Alert
This is a historical content for Windows NT 4.0 product and is presented for informative purposes only. All content in this directory is copyrighted and owned by Microsoft.Processing Certificate Requests
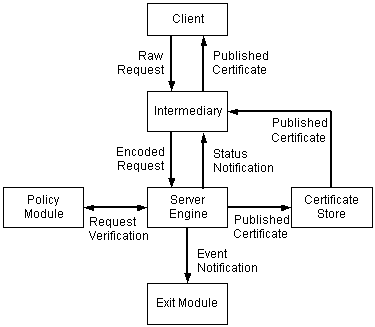
Microsoft® Certificate Server performs the following steps when processing a certificate request:
-
Request reception. The certificate request is sent by the client to an intermediary application, which formats it into a PKCS #10 format request and submits it to the Server Engine.
-
Request approval. The Server Engine calls the Policy Module, which queries request properties, decides whether the request is authorized or not, and sets optional certificate properties.
-
Certificate formation. If the request is approved, the Server Engine takes the request, and any properties requested by the Policy Module, and builds a complete certificate.
- Certificate publication. The Server Engine stores the completed certificate in the certificate store and notifies the intermediary application of the request status. If the exit module has so requested, the Server Engine will notify it of a certificate issuance event. This allows the exit module to perform further operations such as publishing the certificate to a directory service. Meanwhile, the intermediary gets the published certificate from the certificate store and passes it back to the client.
The following diagram illustrates how a certificate request is processed by Certificate Server: